Histamine Intolerance: DAO Supplements & Testing
Histamine intolerance can significantly impact one's quality of life, presenting with various symptoms that may be difficult to manage. Second Opinion Physician is a telehealth practice specializing in diagnosing and addressing health conditions associated with histamine excess, methylation imbalances, and mood-related disorders. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the role of diamine oxidase (DAO) in histamine metabolism, factors contributing to low DAO levels, and the association between gut health and inflammation. Also discussed are dietary and lifestyle strategies to manage histamine intolerance and provide guidance on supplements and lab testing to optimize histamine metabolism.
Understanding DAO and Histamine Intolerance
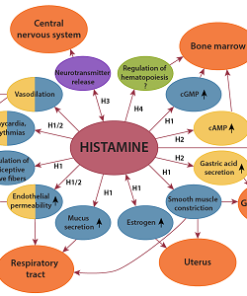
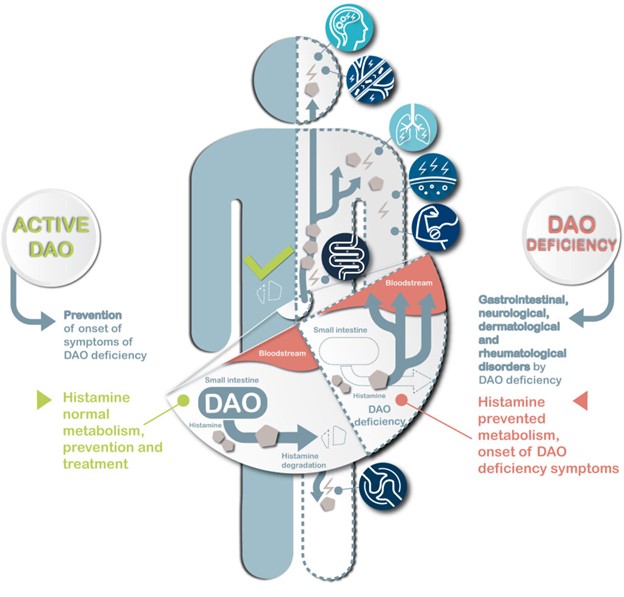
Diamine oxidase (DAO) is an enzyme that is primarily involved in the metabolism and breakdown of histamine in the human body. It is found in various tissues and cells, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys.
Diamine oxidase (DAO) is produced in various tissues and cells throughout the body. The primary sites of DAO production include:
- Gastrointestinal tract: DAO is mainly synthesized and secreted by specialized cells in the intestinal mucosa, particularly in the small intestine, where it plays a crucial role in breaking down histamine in ingested food.
- Kidney: DAO is also produced in the kidneys, where it contributes to histamine metabolism and helps maintain proper histamine levels in the body.
- Placenta: DAO is produced in the placenta during pregnancy to help protect the developing fetus from potential histamine-related issues.
- Other tissues: DAO can be found in lower concentrations in other tissues, such as the skin, liver, and lungs, where it participates in histamine regulation.
It's worth noting that the expression and activity of DAO can be influenced by genetic factors, lifestyle, and diet. Some individuals may have lower levels of DAO, leading to a reduced capacity to metabolize histamine, which can contribute to histamine intolerance.
Factors Contributing to Low DAO Levels
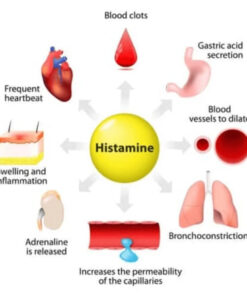
Low levels of diamine oxidase (DAO) can result in histamine intolerance, as the body's ability to break down histamine becomes impaired. Symptoms of histamine intolerance vary from person to person, but some common symptoms associated with low DAO levels include:
- Skin symptoms: itching, hives, redness, eczema, or flushing
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, gas, or nausea
- Respiratory symptoms: nasal congestion, sneezing, runny nose, or difficulty breathing
- Cardiovascular symptoms: irregular heartbeat, palpitations, or low blood pressure
- Neurological symptoms: headaches, migraines, dizziness, or fatigue
- Psychological symptoms: anxiety, irritability, or insomnia
It's important to note that these symptoms can be caused by various factors and not just histamine intolerance or low DAO levels.
Gut Permeability, Inflammation, and DAO Deficiency
Gut permeability and inflammation can impact DAO (diamine oxidase) production and function, although they may not necessarily lead directly to a deficiency in DAO due to an excessive need for histamine metabolism. The relationship is more complex and multifactorial.
Increased gut permeability, also known as "leaky gut," can result from inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract caused by various factors such as food sensitivities, infections, or autoimmune conditions. This altered gut permeability may negatively affect DAO production and release, contributing to an imbalance in histamine levels and exacerbating histamine intolerance symptoms.
Inflammation in the gut may also impair the function of enterocytes, the specialized cells in the intestinal lining that produce DAO. This can lead to reduced DAO secretion into the intestinal lumen, where it is needed to break down histamine. Additionally, inflammation might compromise the overall health of the gut lining, which could indirectly affect histamine regulation.
However, it's essential to note that gut permeability and inflammation are just two of many factors that can influence DAO levels and histamine metabolism. Genetics, diet, and medication use can also play a significant role in determining an individual's DAO levels and histamine tolerance.
If you suspect that you have histamine intolerance or issues related to gut permeability and inflammation, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Addressing Gluten and Dairy Sensitivities in Histamine Intolerance
There isn't a direct relationship between gluten or dairy sensitivity/allergies and DAO (diamine oxidase) levels. However, certain indirect connections exist that can cause overlapping symptoms or exacerbate histamine intolerance in people with low DAO levels.
Gluten sensitivity, commonly seen in conditions such as non-celiac gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, occurs when individuals experience adverse reactions to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Dairy sensitivity or allergies involve negative reactions to lactose or specific proteins, like casein or whey, found in milk and other dairy products.
Here are some indirect associations between gluten/dairy sensitivity and DAO:
- Inflammation: Gluten and dairy sensitivity can cause inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. This inflammation may impact DAO production or activity, worsening histamine intolerance in those with already low DAO levels.
- Impaired gut barrier function: Gluten or dairy sensitivity can lead to increased intestinal permeability or "leaky gut," which may impair the release of DAO into the intestinal lumen where it is needed to break down histamine.
- Overlapping symptoms: Symptoms of gluten or dairy sensitivity, such as bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue, can overlap with histamine intolerance symptoms, making it challenging to distinguish between the two conditions.
- Histamine-rich foods: Some dairy products, such as aged cheeses, contain higher levels of histamine, which can exacerbate symptoms in individuals with low DAO levels.
Managing Histamine Intolerance: Dietary and Lifestyle Strategies
Below is a list of factors that can contribute to low DAO levels. The major category factors include medications, diet, inflammation, autoimmune conditions, gut health, and genetics:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Aspirin, ibuprofen, and other NSAIDs can interfere with DAO function.
- H2-receptor antagonists: Medications like cimetidine and ranitidine used for treating acid reflux can reduce DAO activity.
- Antidepressants: Some tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may affect DAO levels.
- Immunosuppressive drugs: Medications like corticosteroids, used to treat inflammation, may impact DAO production.
- Diuretics: Medications that increase urine output, such as furosemide, can reduce DAO levels.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can impair DAO function and trigger histamine release.
- Histamine-rich foods: Foods like aged cheeses, fermented products, and cured meats can exacerbate histamine intolerance due to their high histamine content.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation, especially in the gastrointestinal tract, can impair DAO production and function.
- Autoimmune conditions: Some autoimmune diseases, like celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease, can impact DAO production and gut health.
- Gastrointestinal infections: Infections that affect the gut, such as Helicobacter pylori, may lead to reduced DAO activity.
- Gut dysbiosis: Imbalanced gut microbes can contribute to gut inflammation, affecting DAO levels.
- Leaky gut syndrome: Increased gut permeability can impact DAO production and release.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins B6, B12, or C and minerals like copper and zinc may affect DAO production and activity.
- Stress: Chronic stress can have a negative impact on overall gut health and DAO production.
- Genetic factors: Certain genetic polymorphisms can result in reduced DAO production or activity.
- Hormonal imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones like estrogen may influence DAO levels.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to allergens or toxins can trigger histamine release and affect DAO activity.
- Liver health: The liver plays a role in histamine metabolism; impaired liver function may reduce DAO levels.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can contribute to inflammation and affect histamine regulation.
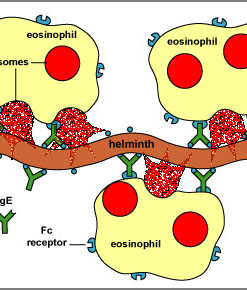
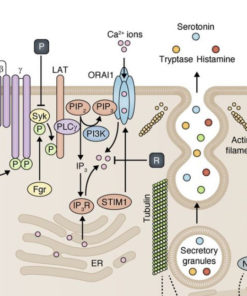
- Mast cell disorders: Conditions characterized by excessive mast cell activation, such as mastocytosis, can lead to increased histamine release, potentially overwhelming the body's DAO capacity.
Managing Histamine Intolerance: Dietary and Lifestyle Strategies
Improving DAO levels and supporting histamine metabolism can be achieved through various lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and targeted supplementation. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Follow a low-histamine diet: Limiting or avoiding histamine-rich foods like aged cheeses, fermented products, cured meats, and alcohol can help manage histamine intolerance.
- Consume DAO-enhancing foods: Some foods, like fresh vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins, can support histamine metabolism.
- Maintain a balanced gut microbiome: Consuming probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt, kefir, or fermented vegetables, can help support a healthy gut environment and enhance DAO production.
- Manage stress: Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help promote overall gut health and support DAO function.
- Ensure adequate nutrient intake: Consuming a balanced diet that provides essential nutrients like vitamins B6, B12, and C, and minerals like copper and zinc, can support histamine metabolism and DAO production.
- Support liver health: Adopting a liver-friendly diet, limiting alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy body weight can support liver function and improve histamine metabolism.
- Avoid medications that interfere with DAO: Consult your healthcare professional before discontinuing any medication, but be aware of medications that can negatively impact DAO function, such as certain NSAIDs, diuretics, or antidepressants.
- Address underlying health conditions: Treating health issues like autoimmune diseases, gastrointestinal infections, or mast cell disorders can help improve DAO levels and histamine tolerance.
- Consider supplementation: Under the guidance of a healthcare professional, supplementing with DAO enzyme or nutrients that support DAO production, such as vitamin B6, vitamin C, or copper, can be beneficial.
- Maintain a healthy body weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help reduce inflammation and support histamine metabolism.
DAO Supplements: Aiding Histamine Metabolism
Taking DAO (diamine oxidase) supplements can be a helpful strategy for some individuals dealing with histamine intolerance or low DAO levels. These supplements typically contain the DAO enzyme, which aids in breaking down histamine in the body, thereby reducing symptoms associated with histamine intolerance.
Before using DAO supplements, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your symptoms, medical history, and help determine whether DAO supplementation is appropriate for you. They can also provide guidance on the correct dosage and duration of supplementation.
It's important to note that DAO supplements are not a cure for histamine intolerance, and it's still crucial to address underlying factors contributing to low DAO levels, such as diet, gut health, inflammation, and other health conditions. Incorporating lifestyle changes and dietary modifications, alongside DAO supplementation, can provide a more comprehensive approach to managing histamine intolerance.
As with any supplement, it's crucial to choose a high-quality, reputable brand to ensure that you're getting a safe and effective product. Additionally, keep in mind that supplements can interact with medications or other supplements.
Alternative Supplements for Histamine Regulation
In addition to DAO supplements, there are other supplements that can help reduce or metabolize histamine in the body. These supplements may work by supporting the enzymes involved in histamine breakdown or by providing nutrients essential for histamine metabolism. Here are some supplements that may help:
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a natural antihistamine that can help reduce histamine levels in the blood. It also supports the immune system and acts as an antioxidant.
- Vitamin B6: This vitamin is crucial for the proper function of DAO and histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT), another enzyme involved in histamine metabolism.
- Quercetin: Quercetin is a natural flavonoid found in many fruits and vegetables. It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and can help stabilize mast cells, reducing histamine release.
- Bromelain: This enzyme, found in pineapple, has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects that may help reduce histamine release and alleviate symptoms associated with histamine intolerance.
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC): NAC is an amino acid derivative with antioxidant properties that can help regulate the immune system and may support histamine metabolism.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil and some plant-based sources, omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and may contribute to better histamine regulation.
- Probiotics: Specific strains of beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Bifidobacterium infantis, can support gut health and help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which may indirectly support histamine metabolism.
Low-Dose Naltrexone and Histamine Intolerance
The potential relationship between low-dose naltrexone (LDN) and histamine intolerance is not well-established, but LDN may indirectly influence histamine levels by modulating the immune system and reducing inflammation. LDN works primarily by temporarily blocking opioid receptors, specifically the OGF-OGFr axis, which plays a role in the release of endorphins and enkephalins. Through its immune-modulating and anti-inflammatory effects, LDN could potentially improve gut health, which in turn may support DAO production and histamine metabolism. Additionally, LDN might help stabilize mast cells, reducing the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. Further research is needed to fully understand the connection between LDN and histamine intolerance or DAO levels.
Lab Tests for Histamine, DAO and Inflammation Status
There are several lab tests, in addition to DAO levels, that can help assess histamine levels, inflammation, and overall histamine metabolism status. These tests can provide valuable information to healthcare professionals in diagnosing and managing histamine intolerance or related conditions. Some useful tests include:
- Plasma or urine histamine: Measuring histamine levels in the blood or urine can provide information about the overall histamine burden in the body.
- Tryptase: Tryptase is an enzyme released by mast cells during an allergic reaction or inflammation. Elevated tryptase levels can indicate mast cell activation and increased histamine release.
- Whole blood histamine: This test measures histamine levels in whole blood, which can provide additional insights into histamine metabolism.
- C-reactive protein (CRP): CRP is a marker of inflammation in the body. Elevated CRP levels can indicate the presence of inflammation, which may contribute to histamine intolerance or impaired DAO function.
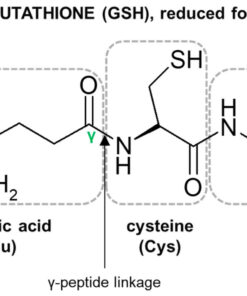
- Glutathione: Glutathione is an antioxidant that plays a crucial role in detoxification and overall immune system function. Assessing glutathione levels can provide information about the body's antioxidant capacity and potential inflammation.
- Complete blood count (CBC): A CBC test provides information on different types of blood cells, which can help assess overall immune system health and detect inflammation or infection.
- IgE levels: Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is an antibody involved in allergic reactions. Elevated IgE levels can indicate the presence of allergies, which may be associated with increased histamine release.
- Food allergy or sensitivity tests: Testing for specific food allergies or sensitivities can help identify potential triggers of histamine release.
- Comprehensive stool analysis: Evaluating the gut microbiome and digestive function can provide insights into potential imbalances that may contribute to histamine intolerance or impaired DAO function.
Summary
Understanding and managing histamine intolerance can be a challenging process, but with the right knowledge and resources, it is possible to improve your quality of life. Second Opinion Physician is dedicated to helping you navigate this journey by offering telehealth services, lab testing, and tailored therapies to address histamine excess, methylation imbalances, and mood-related disorders. By identifying the factors contributing to low DAO levels, implementing dietary and lifestyle changes, and utilizing targeted supplementation and lab testing, you can take control of your health and effectively manage histamine intolerance.
Elevated Histamine and Inflammation Testing
Inflammation
Inflammation
Other Single Item Tests
Walsh Approach Single Tests
Other Single Item Tests
Other Single Item Tests