Histamine, Whole Blood
$65.00
Walsh trained practitioners use whole blood histamine as a marker of methylation status
CPT #83088
Walsh trained practitioners use whole blood histamine as a marker of methylation status. Other practitioners use genetic testing and SNPs of key genes, such as MTHFR as suggestive of methylation status. Both assessments are correct however the influence on histamine levels tell us more about overmethylation than do MTHFR SNPs and are more of a real snapshot of what is happening vs a prediction of what genetically is likely.
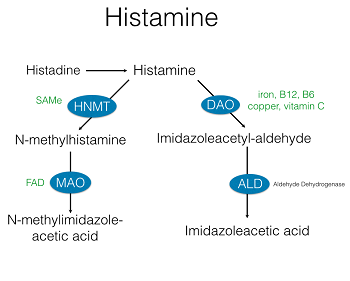
Whole blood histamine is a useful measure of methylation status because histamine methyl transferase, a SAMe regulated enzyme degrades histamine. In the presence of elevated methionine, or SAMe, histamine levels are reduced; which tells us that ‘overmethylated’ synonymous with low histamine. And vice versa, if there are low levels of methionine and SAMe, then histamine is not degraded; an elevated histamine condition is an indication of being ‘undermethylated.’
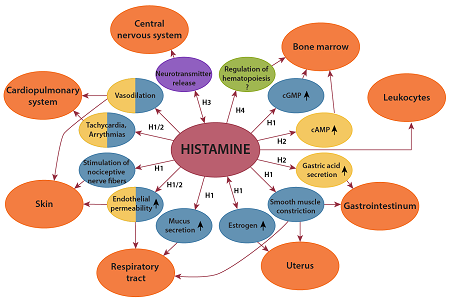
Histamine itself is a neurotransmitter influencing the body with it’s role in the hypothalamus projecting throughout the brain. It increases wakefulness and prevents sleep. During REM and non REM sleep, histamine stops firing completely. Therefore it plays a significant role in the sleep wake cycle.
In the 1950’s the late Carl Pfeiffer, MD recongnized the role of histamine in schizophrenia. From the BIoBalance website it is noted that he found that histapenia, or low histamine was present in as many as 50% of persons with ‘schizophrenia.’
Histapenia – Histamine is an important brain chemical involved in many reactions. It has been found that 50% of patients classified as “schizophrenic” have low histamine levels in the blood and it rises to normal as they improve. These same patients are found to have high copper levels. Elevated copper decreases blood histamine. Excess copper is linked with psychosis. According to Pfeiffer, people with histapenia tend to have classic signs, including canker sores, difficult orgasm with sex, no headaches or allergies, heavy growth of body hair, ideas of grandeur, undue suspicion of people, racing thoughts, the feeling that someone controls one’s mind, seeing or hearing things abnormally, ringing in the ears, and others.
Histadelia – his is a disorder of too much histamine in the blood, noted primarily in males with schizophrenia. It is stimated to affect 15-20% of patients classified as “schizophrenic.” Symptoms include hyperactivity, compulsions, obsessions, inner tensions, blank mind episodes, phobias, chronic depression, and strong suicidal tendencies. Physical signs can include little tolerance for pain, rapid metabolism, lean build, profuse sweating, seasonal allergies, and frequent colds.
Although histamine is small compared to other biological molecules (containing only 17 atoms), it plays an important role in the body. It is known to be involved in 23 different physiological functions. Histamine is known to be involved in many physiological functions because of its chemical properties that allow it to be versatile in binding.