Category: OCD (Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder)
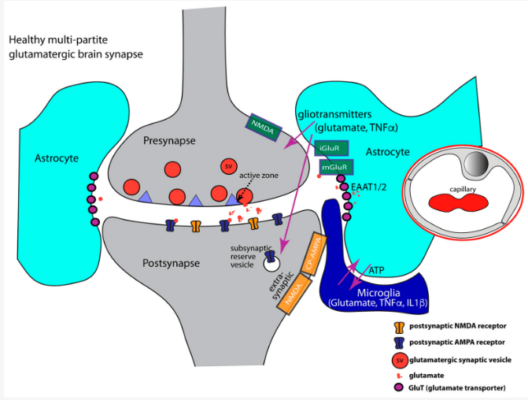
Obsessive–compulsive symptoms often track with NMDAR (NMDA receptor) hyperexcitability in the glutamate system. Excess glutamatergic drive heightens “error signals” in cortico-striatal circuits, feeding intrusive thoughts and compulsive relief behaviors. Undermethylation is frequently present, lowering serotonin/dopamine tone and antioxidant capacity, which further sensitizes NMDAR activity. Posts in this section outline a calming, multi-pathway approach: improve methylation (e.g., SAM or methionine as indicated, zinc, B6), increase glutathione and modulate glutamate with NAC, and use L-theanine and magnesium to reduce receptor overactivation. In refractory cases, NMDAR-modulating medicines such as intranasal ketamine or memantine may be considered under medical supervision. Diet focuses on lowering inflammation and limiting high-glutamate additives (MSG, hydrolyzed/“autolyzed” proteins, yeast extract), ultra-processed foods, and excess aspartame, while emphasizing Mediterranean-style meals that support gut integrity. Additional triggers that can activate/sensitize NMDAR—chronic stress and sleep loss, infections/inflammation (e.g., PANS/PANDAS), and environmental toxins—are addressed through stress hygiene, sleep regularity, and gentle detox support. The goal is to reduce glutamatergic noise, stabilize circuits, and ease OCD symptom pressure.
Ketogenic Therapy for OCD: Ketones not Glucose
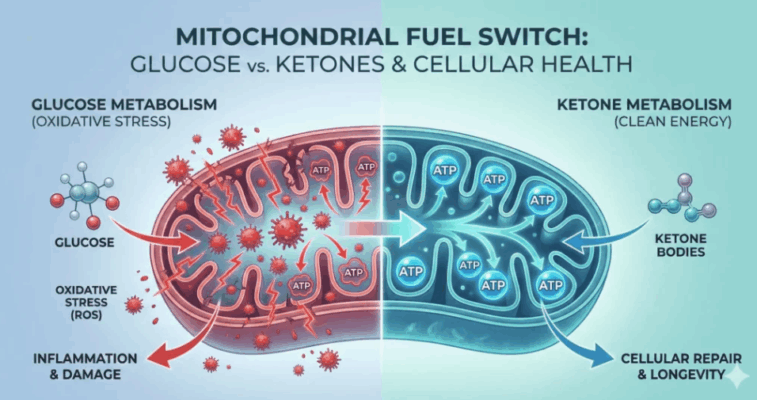
SECOND OPINION SERIES Ketones Not Glucose: The Metabolic Mechanism Behind Ketogenic Therapy for OCD Many [...]
Natural Treatment for OCD Symptoms | Understanding Glutamate, NMDAR & Biochemical Patterns
SECOND OPINION SERIES Natural Treatment for OCD Symptoms | Understanding Glutamate, NMDAR & Biochemical Patterns [...]
Healthy Diet for OCD & Depression
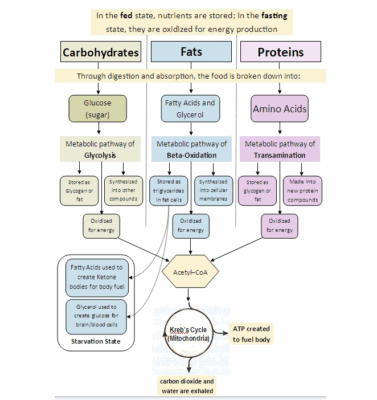
HEALTHY DIET FOR OCD AND DEPRESSION: A DIET AND RECIPE FOR MITOCHONDRIAL SUPPORT This diet [...]
OCD Methylation and Mitochondria: Ketone Ester Therapy
OCD Methylation and Mitochondria: Ketone Ester Therapy & Metabolic Treatment OCD methylation and mitochondria are [...]
Identify Hidden Glutamates in Your Diet to Improve Brain Function
As research into the complexities of the human brain continues, one finding stands clear: dietary [...]