Vitamin D, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (Calcifediol)
$35.00
Vitamin D #82306
Vitamin D, 25-Hydroxy (Calcifediol)
What this test measures
This test measures 25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcifediol), the primary circulating form of vitamin D and the most accurate marker of overall vitamin D status in the body.
It reflects vitamin D obtained from:
-
Sun exposure
-
Diet
-
Supplements
and how effectively vitamin D is being stored and made available to tissues.
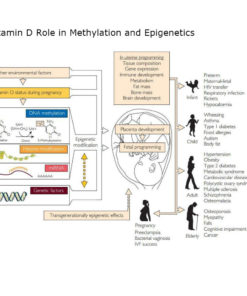
Why vitamin D matters far beyond bone health
Vitamin D functions more like a regulatory hormone than a simple vitamin. It influences hundreds of genes involved in immune balance, brain function, inflammation control, and cellular repair.
Adequate vitamin D is essential for:
-
Nervous system stability and neuroprotection
-
Immune regulation (calming overactive immune responses)
-
Inflammation control
-
Hormone signaling and receptor sensitivity
-
Mood, sleep regulation, and stress tolerance
Deficiency is common—even in people who eat well or supplement—and often goes unnoticed.
Vitamin D and the brain
Vitamin D plays a direct role in:
-
Neurotransmitter regulation
-
Neuroinflammation control
-
Protection against excitatory overstimulation
Low levels are frequently associated with:
-
Sleep disruption
-
Anxiety or inner tension
-
Sensory sensitivity
-
Cognitive slowing or brain fog
-
Poor stress resilience
In neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric presentations, vitamin D deficiency can amplify existing biochemical vulnerabilities rather than act as a single cause.
Vitamin D and immune balance
Vitamin D helps the immune system respond appropriately—strong when needed, quiet when not.
Low vitamin D may contribute to:
-
Chronic immune activation
-
Poor recovery after infection
-
Heightened inflammatory signaling
-
Increased sensitivity to environmental triggers
This is particularly relevant in individuals with histories of:
-
Autoimmune tendencies
-
Chronic inflammation
-
Mold or toxic exposures
-
Recurrent infections
Why vitamin D is included in the Walsh Comprehensive Biotype Panel
Within a Walsh-informed framework, vitamin D is considered a foundational regulator, not an isolated variable.
Vitamin D status influences:
-
How the nervous system responds to stress
-
Inflammatory tone affecting neurotransmitter balance
-
Expression of symptoms that overlap with methylation, copper imbalance, or oxidative stress
Without knowing vitamin D status, other biochemical findings can be misleading or incomplete.
Low vs high vitamin D — both matter
-
Low levels may impair immune control, brain signaling, and recovery capacity
-
Excessively high levels (usually from unsupervised supplementation) can disrupt calcium balance and increase oxidative stress
Testing ensures vitamin D support is appropriate, targeted, and safe.
Why testing is important (not guessing)
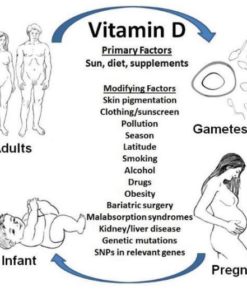
Vitamin D requirements vary widely between individuals based on:
-
Genetics
-
Body composition
-
Sun exposure
-
Absorption efficiency
-
Inflammatory burden
Symptoms alone do not reliably predict vitamin D status. Testing provides clarity before making long-term decisions.
Who should consider this test
-
Individuals with sleep, mood, or stress-related symptoms
-
Those with inflammatory, immune, or neurological concerns
-
Anyone with limited sun exposure or long-term supplementation
-
Individuals pursuing a Walsh-based biochemical assessment
Testing details
-
Blood test
-
Measures 25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcifediol)
-
Performed through Labcorp
-
After purchase, a Labcorp requisition will be provided for specimen collection
What You Receive
-
A LabCorp order (no doctor’s visit required)
-
Testing at any LabCorp location nationwide
-
Results typically within 2–3 business days
-
Optional review and interpretation through Second Opinion Physician services
-
Guidance on optimal ranges, not just “normal” lab values
How to Use This Test
-
Add the test to your cart and complete checkout.
-
You will receive a LabCorp requisition form by email.
-
Visit any LabCorp site for a quick blood draw.
-
Results will be delivered securely through your patient portal.
-
You may schedule a follow-up consult for interpretation and a personalized plan.
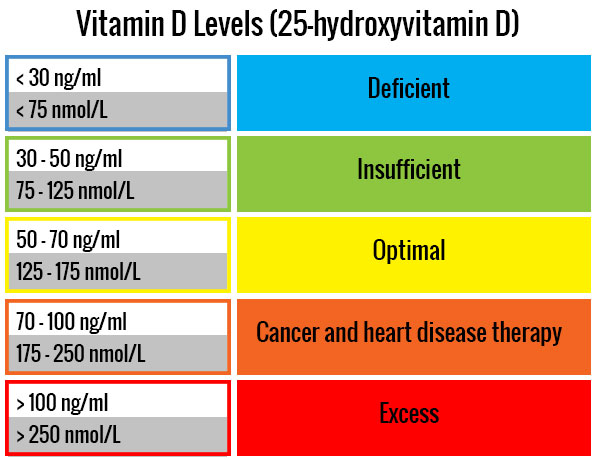
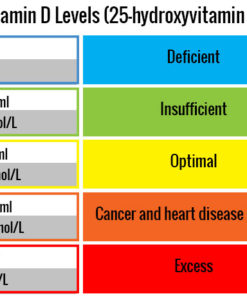
Optimal Levels
While labs often report wide “normal” ranges, research and clinical practice commonly support:
-
50–90 ng/mL as an optimal functional range
-
Levels below 30 ng/mL indicate deficiency
-
Levels below 20 ng/mL significantly increase risk of infection, mood issues, and bone loss